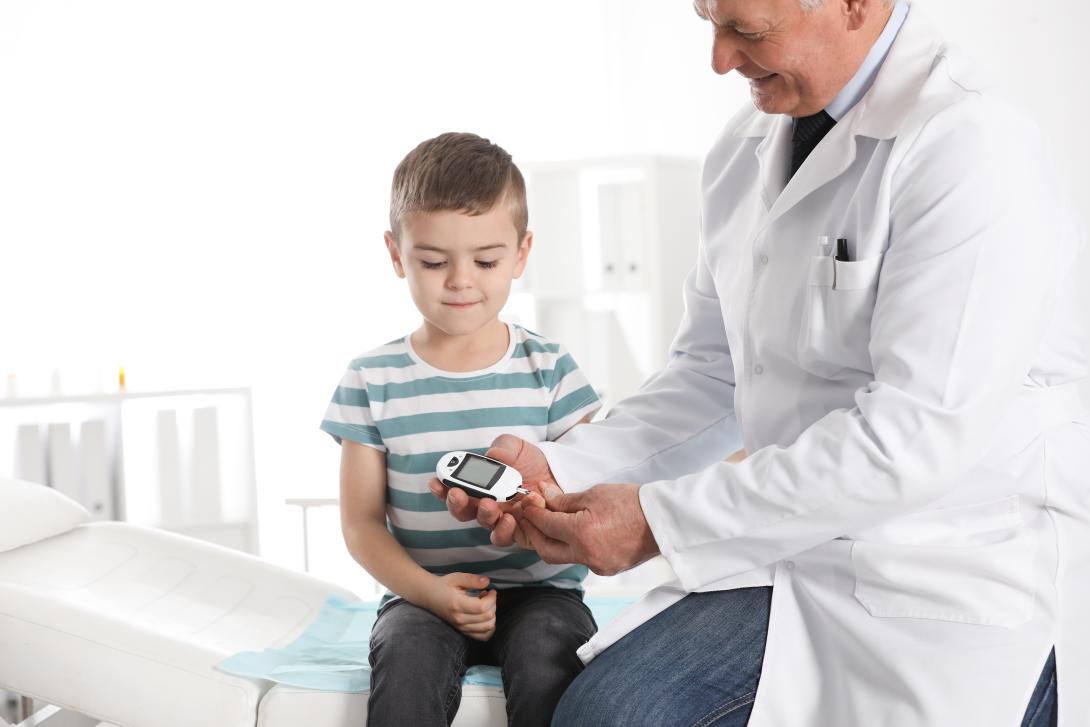
Learn about type I Diabetes Mellitus (Juvenile Diabetes)
If your child have recently been diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus, you will certainly felt like you are losing the earth under your feet! However, you should know that Diabetes Mellitus is not a rare condition. It affects a significant number of children and can be treated very effectively.
What is Juvenile Diabetes?
The inability of the human body to adequately regulate blood glucose levels is called Diabetes Mellitus. Blood glucose levels may range from 80 - 110 mg/dl. After a meal, glucose levels rise and through the beta cells of the pancreas, the body produces insulin, which regulates glucose levels within normal limits. In pathological situations, cases are distinguished in type I, where the body does not produce sufficient amounts of insulin and Type II where the body produces insulin, but its action is resisted. In children cases, the most frequent phenomenon is the appearance of Diabetes Mellitus Type I or juvenile diabetes as it is also called; this condition is characterized by the reduced ability of the body to produce insulin in the pancreas.
Signs and symptoms of juvenile diabetes
Diabetes is caused by genetic predisposition. Namely, it is caused by a gene inherited by the child and which at some stage of its life is manifested. The onset may occur after a viral infection and is not due to the child's diet or consumption of sweets. Of course, some factors, such as the environment or the existence of obesity can accelerate it, but is not due to them. In fact, the biological processes and antibodies in the child's blood that act against the pancreas cells have started long before the onset of the disease.
It is important that everybody knows the symptoms of juvenile diabetes or diabetes type I, to allow a diagnosis as early as possible and to prevent diabetic coma. The symptoms are
• Increased thirst and frequent urination
• Excessive and frequent hunger
• Weight loss
• Fatigue
• Irritability and unusual behaviour
• Impaired vision (blurred vision)
• Frequent presentation of genital yeast infection (for girls)
What is the treatment of juvenile diabetes?
Unfortunately, type I diabetes mellitus, is still incurable. But it can be treated effectively using appropriate amounts of insulin in combination with an appropriate diet. The process requires good training of parent and child, so that they know in detail how to feed it. Do not assume that the child will not be able to consume a sweet or another carbohydrate-rich food. You must simply learn to count the grams of carbohydrate and accordingly adjust the insulin dose. The same applies to any other snack that can be found at a party or even to fruits, that also contain carbohydrates. No doubt, Diabetes treatment in children is a challenge, since the child can not easily understand the need for measuring blood glucose levels or the insulin administration. Thus in practice children can become frustrated, fearful or even less cooperative. So the first challenge is to achieve cooperation with the child and then the treatment becomes much easier.
Last but not least, a significant parameter in the overall treatment of the situation is the attitude of the family. The family can make food choices and the new way of the life of the child to look easy, while at the same time every member of the family will be benefited. It is therefore necessary to create healthy eating habits with regular meals, correct choices of food and raw materials and to have common activities that will include physical exercise
Advice
The nutritional information and recommendations on infant-toddler diet are indicative and refer to general guidance for this age group. Time that every child can be introduced to solid foods or add more to it’s diet, must be individualized. We recommend to set advise from your pediatrician about the specific nutritional needs of your child.